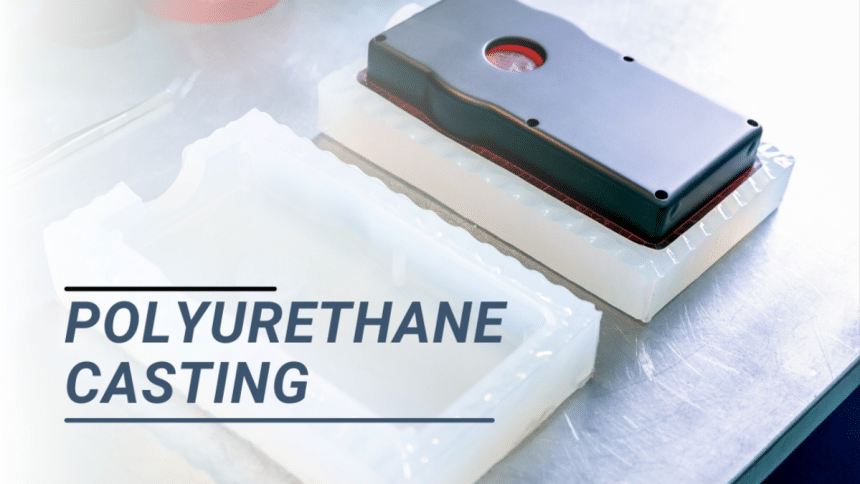
Intrigued about a technique where liquefied substances turn into solids? Polyurethane casting is an efficient solution. The process is relatively cheap and provides extremely resilient products. It’s suitable for making parts in small production. The quality of the products, produced in a particular line should not vary at all. Moreover, customization is possible through polyurethane vacuum casting.
What Is Polyurethane Casting?

Urethane Casting
Polyurethane casting also known as vacuum casting, is a technique used in designing prototypes. It’s a Low-volume manufacturing process. Usually applicable in the production of up to 25 pieces. Another name used for the polyurethane casting process is urethane casting. Three primary steps comprise the polyurethane vacuum casting process: These include the creation of the master, the making of silicone mold, and fashioning castings.
- Master Creation: Designers use techniques such as CNC machining or stereolithography 3D printing, known as SLA 3D printing. A positive master pattern of the required part is created. In this case, any solid material is suitable to be used as a pattern. The intended material has to be able to endure temperatures of 40°C during silicone curing.
- Mold Making: A casting box is half-filled with liquid silicone. This box has a pattern sitting in the middle of it. The silicone cures at low heat for 16 hours creating a rigid half of the mold or the upper half of the mold. To this casting box, more liquid silicone is poured until the box is full to the brim. The second half of the mold is made by silicon curing. Subsequently, it is possible to free the mold halves, and the pattern can be used again, if necessary.
- Casting Process: The vacuum casting plastic resin is received in flexible silicone molds. This resin then hardens in that mold and will then take the shape of the predesigned master. On estimation, one mold can produce 25 of the castings before the silicone mold replacement.
Polyurethane casting is useful because silicone molds are inexpensive. They are much cheaper than the traditional metal tooling prices in the market. Their life span is about 25 castings, which in most cases is enough to produce a small plastic part for prototyping.
In addition, casting polyurethane resins are not necessarily high function parts but they have their specialties. The process delivers a high-quality surface finish, allows for the use of a range of colors and opacity, and is still economical for small production runs.
Understanding Tolerances and Design Considerations for Polyurethane Casting
The current requirement for the production of polyurethane cast parts includes specified tolerances and dimensions. Understanding these differences is crucial to achieving a good prototype and end-use product.
Tolerances:
In vacuum casting, it’s highly crucial to attain the right tolerance level. Dimensions can be held to within ± 0.3% of the nominal size, with a minimum of ± 0.3 mm for parts under 100mm in size.
Shrinkage:
Polyurethane casting, however, causes some parts to shrink more where the molding temperatures vary, especially when molding is thick. A shrinkage rate of about + 0.15% should be provided in the design stage.
Part Size:
Polyurethane cast parts: maximum size is 1900mm x 900mm x 750mm, total volume – up to 10 liters.
Wall Thickness:
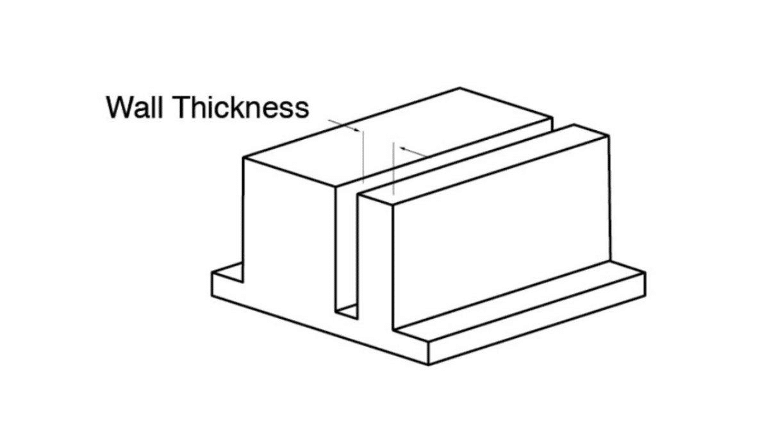
Wall Thickness For Vacuum Casting
The minimum thickness of the wall required for mold filling is about 0.75mm. The wall thickness must be kept as high as 1.5mm or more to get better efficiency.
Draft Angles:
The removal of the finished parts doesn’t require ejector pins due to the flexibility of silicone molds. It’s not obligatory to have draft angles, but it’s important to have a small draft of not over 5° to prolong the mold’s service. It also enables future designs to easily transfer to injection molding.
Radii:
To increase the strength and stability of the structure, it is highly necessary to avoid sharp internal corners. It would be desirable to add fillets with a radius of not less than 3 mm to strengthen these corners.
Ribs:
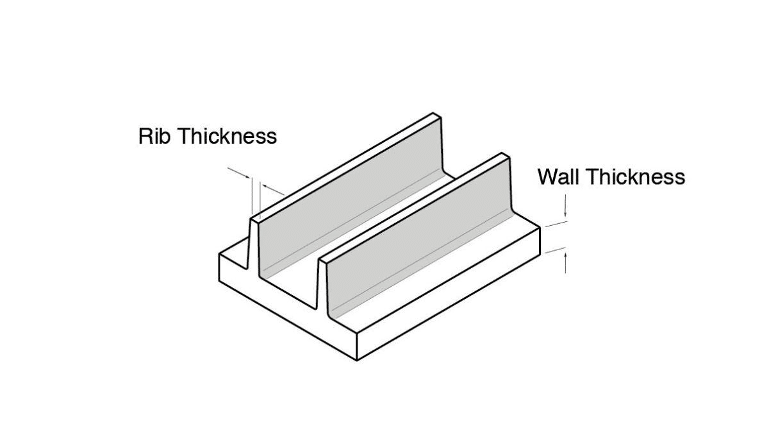
Rib Thickness
Ribs can be incorporated into designs such that they can help increase the stiffness of a structure while affecting the thickness of the walls, simultaneously. It’s better to use several short ribs, and the orientation of these ribs to possible bending points is critical.
Bosses:
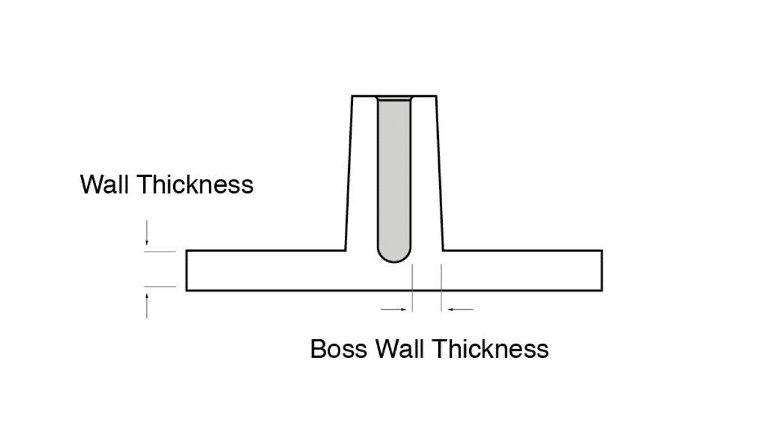
Bosses In Design
Parts can be designed to have protrusions that will hold fasteners. To prevent sink marks, bosses should be thin-walled. These preferably with a thickness of less than 60% of the total wall thickness of the particular part.
Threads and Holes:
It’s possible to use through holes and threads in polyurethane casting. To incorporate these features, using inserts is the most efficient approach to getting them done, due to the efficiency of manufacturing.
Joints:
Tongue-and-groove joints can be employed to join the multi-component parts of an assembly. It’s advised to have a small gap between the reveal to ensure the components fit properly.
Surface Features:
It’s possible to add text/logos to cast parts. Better still, these features are best engraved through CNC-machined master patterns as opposed to 3D-printed master patterns.
General Polyurethane Casting Problems
As with any craft, polyurethane casting has its peculiarities. Lumens, cracks, and other related problems are likely to happen during the casting process. However, these difficulties are manageable by using some techniques and adequate knowledge to obtain successful outcomes. It’s feasible to foresee certain problems in both small home improvement and complex industrial ventures. Having the tools to troubleshoot will help deal with these issues.
Bubbles and Imperfections: Prevention and Solutions
The bubbles formation in polyurethane casting is quite common. This is especially so when humidity comes into contact with the vacuum casting materials. To eliminate the problem of the formation of air bubbles, using a vacuum chamber to remove the air from the mixed polyurethane is very useful. Although the bubbles are still produced even by hand mixing, the degree of their formation is greatly minimized here.
Also, the PolyCoat, silicone-based sealer and release agent applied to polyurethane rubber molds can help to produce smoother surfaces. It will not only reduce the amount of air bubbles but also help with the painting process. Another useful technique involves the use of a syringe with a fine-point needle for the resin injection into the mold. In this technique, air entrapment is effectively controlled, and the number of additional vent holes required is also reduced.
Mitigating Factors in Environmental Analysis
Another difficulty in polyurethane casting is environmental factors. External factors like temperature and humidity, play an important role in the casting process quality. For instance, low temperatures enhance the pot life of the urethane products since reactions are reduced.
These environmental influences have to be recognized and assimilated if one wants the best results in the casting process. Any changes to pot life and curing times should be made dependent on the prevailing circumstances. It’s advisable to seek out reliable vacuum casting service providers to achieve the desired castable parts/products.
Common Applications of Polyurethane Castings
Polyurethane castings are extremely versatile and can be used in almost every industry imaginable. In product design, they have the responsibility of developing models and actual products. It also gives designers the advantage of improving the design since prototypes and the final parts are made from the same material.
Polyurethane castings are used in medical applications, especially in the making of complex and strong parts. They are applied in the construction of individual prostheses, and preparing models for surgery.
Aside from medical uses, polyurethane castings are used in most consumer products. They can be used in ornaments or everyday appliances and utensils. From the vehicle you use to get to work to the furniture you use in your home, polyurethane castings add value to numerous products consumers use.
Key Takeaways & Recommendations
Polyurethane casting utilizes flexible urethane resins. It offers an opportunity to select from various options in terms of hardness and load-bearing characteristics. It’s important to pay significant attention to finer details for the polyurethane casting to obtain successful outcomes. Accurate work area preparation allows for appropriate mixing. Since it directly impacts the quality of the casting product. Moreover, controlling the pot life and the time of curing also plays a critical role in process effectiveness.
However, different challenges in polyurethane casting can be controlled adequately. Some problems generally found include the air bubbles formation in the material. The best ways of minimizing bubbles include the application of degassing procedures. Temperature changes increase the total casting process productivity. The resin type to be used in the vacuum casting project must be set at the right hardness and viscosity.